Car Body: An Introduction to Basic Terms and Concepts
When it comes to understanding the different parts of a car, one of the most important components to consider is the car body. The car body refers to the outer shell of the vehicle, which provides protection to the internal components and passengers. It plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and structural integrity of the car.
The car body is made up of various materials, such as steel, aluminum, or carbon fiber, depending on the make and model of the vehicle. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and weight considerations. The body is designed to withstand different types of forces, including impacts, vibrations, and torsion, while also providing an aerodynamic shape to improve fuel efficiency.
There are several key terms and concepts related to the car body that are important to understand. One of these is the chassis, which is the framework that supports the car body. It provides the structural strength and rigidity to the vehicle, allowing it to handle various road conditions and stresses. The chassis is typically made of steel or aluminum and is designed to distribute the forces evenly throughout the vehicle.
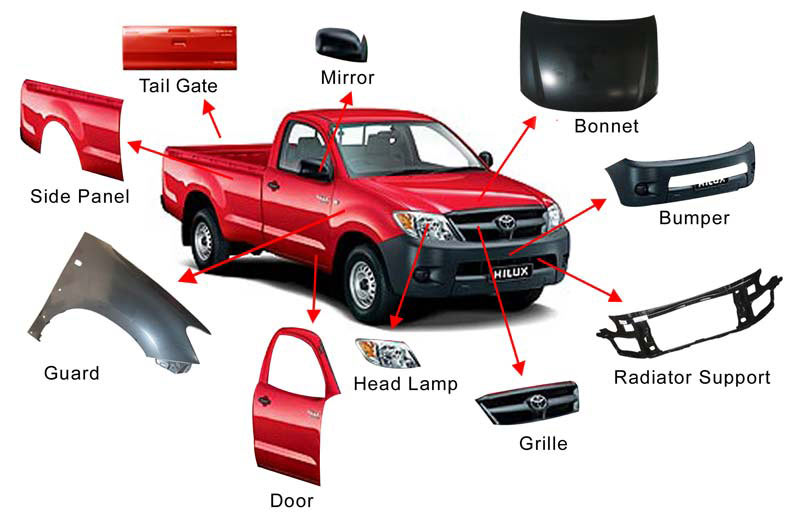
Another important term is the body panels, which are the individual components that make up the car body. These panels include the roof, doors, fenders, and trunk, among others. They are usually made of metal and are attached to the chassis using various methods, such as welding or bolting. The body panels not only provide the aesthetic appeal to the car but also contribute to its overall strength and protection.
What is a car body?
The car body refers to the outer shell of a vehicle, also known as the “body shell” or “bodywork”. It is the main component that gives the vehicle its shape and provides protection to the passengers and the mechanical components inside.
The car body is typically made of metal, such as steel or aluminum, although some modern cars also incorporate materials like carbon fiber or fiberglass to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. The body is designed to be aerodynamic, reducing drag and improving the overall performance of the vehicle.
Within the car body, there are various structural components, such as the frame, which provides strength and rigidity, and the panels, which make up the exterior surface of the vehicle. These panels can be removable for easy access to the engine or other mechanical parts.
The car body also includes features such as doors, windows, and the roof, which provide access to the interior and protect the occupants from the elements. Additionally, the body may have features like fenders, bumpers, and grille, which not only enhance the appearance of the vehicle but also provide protection in case of a collision.
Overall, the car body plays a crucial role in the design, functionality, and safety of a vehicle. It is not only responsible for providing protection to the occupants but also contributes to the overall performance and aesthetics of the car.
Car body definition
The car body refers to the outer shell or structure of a vehicle. It is the part of the car that gives it its shape and protects the internal components. The body is typically made of metal or a combination of materials, such as steel, aluminum, and plastic.
The car body plays a crucial role in providing strength and rigidity to the vehicle, ensuring safety for its occupants. It also contributes to aerodynamics, which affects the car’s fuel efficiency and performance.
Various components make up the car body, including the roof, doors, hood, trunk, fenders, and bumpers. These parts are designed to fit together seamlessly, creating a cohesive and visually appealing design.
Car bodies can be categorized into different types, such as sedans, coupes, SUVs, and hatchbacks, each with its unique characteristics and purposes. The design and style of the car body can vary greatly, reflecting the manufacturer’s branding and customer preferences.
Overall, the car body is an essential element of a vehicle, providing structural integrity, protection, and aesthetics.
Functions of a car body
The car body serves several important functions in a vehicle. These functions include:
1. Enclosing the passenger and cargo compartments: The car body acts as a protective shell that encloses the passenger and cargo compartments. It provides a barrier between the occupants and the external environment, protecting them from weather conditions, road debris, and other hazards.
2. Supporting the vehicle’s structural integrity: The car body provides structural support to the vehicle, ensuring its stability and rigidity. It helps distribute the forces generated during acceleration, braking, and cornering, preventing the vehicle from collapsing or deforming under stress.
3. Enhancing aerodynamics: The car body is designed to minimize air resistance and improve the vehicle’s aerodynamic performance. Smooth and streamlined shapes help reduce drag, allowing the car to move through the air more efficiently and achieve better fuel efficiency.
4. Absorbing and dissipating impact energy: In the event of a collision, the car body absorbs and dissipates the impact energy, protecting the occupants inside. This is achieved through the use of crumple zones and other safety features that deform and absorb the energy, reducing the forces transmitted to the passenger compartment.
5. Providing mounting points for various components: The car body serves as a platform for mounting various components, such as the engine, suspension, and drivetrain. It provides the necessary attachment points and supports for these components, ensuring their proper functioning and integration within the vehicle.
Overall, the car body plays a crucial role in the performance, safety, and functionality of a vehicle. It combines aesthetics with engineering principles to create a structure that meets the needs of both the driver and the passengers.
What are the types of car bodies?
There are several types of car bodies, each with its own unique design and characteristics. Here are some of the most common types:
- Sedan: A sedan is a four-door car with a separate trunk space. It is the most common type of car body and is known for its spacious interior and comfortable seating.
- Hatchback: A hatchback is a car body that has a rear door with a rear window that can be opened. It typically has a compact design and a smaller trunk space.
- SUV: An SUV, or sports utility vehicle, is a larger car body that is designed for off-road capabilities. It usually has a higher ground clearance and a more rugged exterior.
- Coupe: A coupe is a two-door car body with a sloping roofline and a sporty design. It is often associated with performance and luxury.
- Convertible: A convertible is a car body that has a retractable roof, allowing the driver to enjoy an open-air driving experience. It is often considered a symbol of luxury and style.
- Minivan: A minivan is a larger car body that is designed to transport multiple passengers. It has a boxy shape and a spacious interior, making it ideal for families or groups.
- Pickup truck: A pickup truck is a car body that has an open cargo area at the back, allowing it to carry heavy loads. It is often used for transportation and hauling purposes.
These are just a few examples of the different types of car bodies available. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of car body often depends on the individual’s preferences and needs.
Sedan
A sedan is a type of car body style characterized by a separate trunk compartment for cargo storage. It is one of the most common car body types and is known for its practicality and spaciousness.
The sedan typically has four doors and can seat up to five passengers comfortably. It is designed to prioritize passenger comfort and safety, with ample legroom and headroom in both the front and rear seats.
Sedans come in different sizes, from compact sedans to full-size sedans. Compact sedans are smaller in size and offer better fuel efficiency, while full-size sedans are larger and provide more interior space.
One of the advantages of a sedan is its versatility. The separate trunk compartment allows for easy storage of luggage, groceries, and other items without compromising the passenger cabin. Sedans are also known for their stability and smooth ride, making them a popular choice for everyday commuting and long-distance travel.
In recent years, sedans have incorporated advanced safety features and technology, such as lane departure warning, blind spot detection, and adaptive cruise control. Many sedans also offer luxurious features and options, including leather seats, premium sound systems, and advanced infotainment systems.
Overall, sedans are a popular choice for individuals and families looking for a practical and comfortable car that offers a balance of style, performance, and functionality.
Hatchback
A hatchback is a type of automobile body style that features a rear door that opens upwards and provides access to a cargo area. This door is hinged at the roofline and can be opened independently from the rest of the car’s doors. The cargo area in a hatchback is typically located behind the rear seats and can be expanded by folding down the rear seats, allowing for larger items to be transported.
Hatchbacks are known for their versatility and practicality. They offer a good balance between passenger space and cargo capacity, making them a popular choice for individuals and families. The rear door design of a hatchback also allows for easy loading and unloading of items, as well as quick access to the cargo area.
In addition to their functionality, hatchbacks are also known for their compact size and efficient use of space. They are often smaller and more maneuverable than other types of cars, making them well-suited for city driving and parking in tight spaces.
Hatchbacks can come in various sizes and shapes, ranging from small and sporty models to larger and more spacious ones. Some hatchbacks may have a sloping rear roofline, known as a “fastback” design, while others may have a more upright and boxy shape.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Easy access to cargo area | Less rear headroom for passengers |
| Good balance of passenger space and cargo capacity | Less rear visibility due to the rear door design |
| Compact size and maneuverability | Smaller rear window compared to other body styles |
| Efficient use of space | Limited ground clearance |
Overall, hatchbacks offer a practical and versatile solution for individuals and families who prioritize cargo space and ease of access. Their compact size and efficient use of space make them a popular choice for urban environments, while their various sizes and shapes cater to different needs and preferences.
Station wagon
A station wagon, also known as an estate car or simply a wagon, is a type of car body style that features a longer roofline and a rear cargo area that extends beyond the rear seats. The term “station wagon” originated from the early use of these vehicles to transport people and their luggage between train stations.
Station wagons are typically designed with a two-box configuration, consisting of a passenger compartment and a cargo area. The cargo area is accessed through a rear tailgate, which can be either a side-hinged door or a top-hinged door. Some station wagons also feature a rear-facing third row of seats, which can be folded down to increase cargo space.
Station wagons are known for their practicality and versatility. They offer more cargo space compared to sedans and are often used for carrying large or bulky items. Station wagons also provide comfortable seating for passengers, making them popular for family use.
In recent years, the popularity of station wagons has declined in some markets, as consumers have shifted towards SUVs and crossovers. However, station wagons continue to be favored by enthusiasts and those who value their unique combination of style, practicality, and driving dynamics.
Overall, station wagons are a distinct car body style that offers a balance of functionality, comfort, and style.
Coupe
A coupe is a type of car body style that typically has two doors and a fixed roof. It is known for its sleek and sporty appearance. Coupes are often designed with a sloping roofline and a shorter overall length compared to other car body styles.
Coupes are popular among car enthusiasts who value style and performance. They are often associated with luxury and high-performance vehicles. Coupes are designed to provide a more engaging driving experience and are often equipped with powerful engines and advanced suspension systems.
One of the defining features of a coupe is its seating arrangement. Coupes typically have two rows of seats, with the rear seats being smaller and less comfortable compared to those in a sedan. This is because coupes prioritize style and performance over practicality and passenger space.
In recent years, the definition of a coupe has expanded to include four-door models with a coupe-like design. These vehicles, often referred to as “four-door coupes,” have a similar sleek and sporty appearance as traditional coupes but provide easier access to the rear seats.
- Two doors
- Fixed roof
- Sleek and sporty appearance
- Sloping roofline
- Shorter overall length
- Luxury and high-performance
- Engaging driving experience
- Powerful engines
- Advanced suspension systems
- Two rows of seats
- Rear seats are smaller and less comfortable
- Four-door coupe models
SUV
A Sport Utility Vehicle (SUV) is a type of vehicle that combines elements of a traditional passenger car with features from off-road vehicles. SUVs are known for their high ground clearance and large interior space, making them ideal for both city driving and outdoor adventures.
One of the defining characteristics of an SUV is its body style. Unlike sedans or coupes, SUVs have a higher roofline and a more vertical rear end, which allows for increased headroom and cargo capacity. This design also gives SUVs a more rugged and aggressive appearance.
SUVs can be classified into different categories based on their size. Compact SUVs, also known as crossover SUVs, are smaller in size and offer better fuel efficiency compared to larger SUVs. Mid-size SUVs are larger and provide more interior space and towing capacity. Full-size SUVs are the largest and often have three rows of seating, making them suitable for large families or groups.
SUVs are popular for their versatility and ability to handle various driving conditions. Many SUVs come with all-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems, which improve their off-road capabilities. This makes SUVs a popular choice for outdoor enthusiasts or people living in areas with challenging weather conditions.
Due to their size and weight, SUVs typically have a higher center of gravity compared to sedans or hatchbacks. This can affect their handling and stability, especially during sharp turns or sudden maneuvers. However, modern SUVs are equipped with advanced safety features such as electronic stability control and traction control, which help mitigate these issues.
Overall, SUVs are a popular choice for individuals and families who need a vehicle that offers both comfort and versatility. Whether it’s for daily commuting or weekend adventures, SUVs provide a combination of style, space, and capability.
What are the components of a car body?
A car body is made up of various components that work together to provide structure, safety, and aesthetics. These components include:
| Frame | The frame is the main structure of the car body and provides support and rigidity. It is usually made of steel or aluminum and forms the basis for the rest of the components. |
| Body Panels | The body panels are the outer shell of the car body and include the doors, hood, trunk, and fenders. They are usually made of sheet metal and are responsible for the car’s appearance. |
| Bumpers | Bumpers are designed to absorb and redistribute impact energy in the event of a collision. They are typically made of plastic or composite materials and are located at the front and rear of the car. |
| Glass | Glass components, such as the windshield, side windows, and rear window, provide visibility and protection from the elements. They are typically made of laminated or tempered glass. |
| Lights | Lights are essential for visibility and safety. They include headlights, taillights, turn signals, and brake lights. These components are usually made of plastic or glass. |
| Interior | The interior components of a car body include seats, dashboard, steering wheel, and controls. These components provide comfort, convenience, and control for the driver and passengers. |
These are just a few of the main components that make up a car body. Each component plays a vital role in the overall design, functionality, and safety of the vehicle.
Body shell
The body shell of a car is the outer structure that forms the framework of the vehicle. It is commonly made from metal, such as steel or aluminum, and is designed to provide strength, rigidity, and protection to the occupants and components within.
The body shell consists of several key components, including:
- Roof: The top part of the body shell that provides protection from the elements.
- Sides: The panels that form the sides of the car and provide structural integrity.
- Doors: The openings in the body shell that allow access to the interior of the car.
- Front end: The front section of the body shell, which includes the hood, grille, and headlights.
- Back end: The rear section of the body shell, which includes the trunk or tailgate and rear lights.
- Floor: The bottom part of the body shell that supports the weight of the vehicle.
The body shell also includes various structural reinforcements, such as pillars, beams, and cross members, which help distribute the forces in the event of a collision and improve overall safety.
In addition to providing protection and structural integrity, the body shell also plays a role in aerodynamics, as it helps reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency.
Exterior panels
Exterior panels are the outermost layer of a car’s body, covering and protecting the underlying structure. These panels are typically made of metal or composite materials and are designed to be both aesthetically pleasing and durable.
The most common exterior panels on a car include the hood, doors, fenders, roof, trunk, and bumpers. These panels are often painted or coated to provide a smooth and attractive finish.
Exterior panels not only enhance the overall appearance of a car, but they also serve important functional purposes. For example, the hood protects the engine and other mechanical components, while the doors provide access to the interior of the car.
Exterior panels can be subject to damage from accidents, weather conditions, and everyday wear and tear. In such cases, they may need to be repaired or replaced to maintain the integrity and appearance of the car.
Overall, exterior panels play a crucial role in the design, protection, and functionality of a car’s body. They not only contribute to the car’s visual appeal but also ensure its structural integrity and safety.
Glass components
Glass components are an important part of a car’s body. They provide visibility and protection from external elements. Some of the key glass components in a car include:
| Glass Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Windshield | The windshield is the front glass component of a car. It provides a clear view for the driver and protects against wind, rain, and other debris. |
| Side Windows | Side windows are located on the sides of the car. They can be opened or closed and provide visibility to the sides of the vehicle. |
| Rear Window | The rear window is located at the back of the car. It provides visibility to the rear and can be opened or closed. |
| Quarter Glass | Quarter glass is a small triangular-shaped glass component located between the side windows and the windshield or rear window. It provides additional visibility and can be opened or closed. |
| Sunroof | A sunroof is a glass panel located on the roof of a car. It can be opened or closed to allow fresh air and sunlight into the vehicle. |
These glass components are made of specially treated glass that is designed to be strong and resistant to shattering. They are an essential part of a car’s body and contribute to the overall safety and functionality of the vehicle.
What is a unibody?
A unibody, also known as a monocoque structure, is a type of car body construction where the body and frame are integrated into a single unit. Unlike a traditional body-on-frame construction, where the body and frame are separate entities, a unibody design uses the body structure to provide the strength and rigidity required for vehicle operation.
In a unibody construction, the body panels and structural components are designed to work together to distribute and absorb the forces that occur during normal operation, such as acceleration, braking, and cornering. This design approach allows for a lighter and more efficient vehicle, as well as improved handling and safety.
One key advantage of a unibody design is that it allows for more interior space, as the absence of a separate frame allows for a lower floor and larger cabin area. Additionally, unibody construction can provide better crash protection, as the body structure can be designed to absorb and dissipate impact forces more effectively.
However, a unibody design may have limitations in terms of towing capacity and off-road capability, as the integrated body structure may not be as robust as a separate frame. Additionally, repairing a unibody vehicle can be more complex and costly, as damage to the body structure may require extensive repairs or replacement.
Overall, the use of a unibody construction depends on the specific needs and requirements of the vehicle. It is commonly used in passenger cars and crossover SUVs, where the benefits of improved handling, fuel efficiency, and safety outweigh the potential drawbacks.
Unibody design features
A unibody design is a type of construction used in modern cars where the body and frame are integrated into a single structure. This design offers several features and advantages over traditional body-on-frame construction.
Some of the key features of a unibody design include:
| 1. Lightweight construction: | The integration of the body and frame into a single structure allows for a lighter overall weight of the vehicle. This can result in improved fuel efficiency and better performance. |
| 2. Increased structural rigidity: | By eliminating the separate body and frame, a unibody design provides increased structural rigidity. This improves the overall strength and durability of the vehicle, as well as enhances safety in the event of a collision. |
| 3. Enhanced handling and maneuverability: | The unified design of a unibody structure helps to distribute weight more evenly, resulting in improved handling and maneuverability. This allows for better control and responsiveness on the road. |
| 4. Noise and vibration reduction: | The integration of the body and frame in a unibody design helps to reduce noise and vibration. This leads to a more comfortable and enjoyable driving experience. |
| 5. Design flexibility: | Unibody construction offers greater design flexibility compared to body-on-frame construction. This allows for more creative and aerodynamic car designs, as well as improved interior space utilization. |
Overall, the unibody design features contribute to the modern car’s performance, safety, comfort, and aesthetics.
Advantages of unibody construction
Unibody construction, also known as unitized construction, is a design technique used in the automotive industry where the body and chassis of a vehicle are integrated into a single structure. This approach offers several advantages over traditional body-on-frame construction:
- Lighter weight: Unibody construction typically results in a lighter overall vehicle weight compared to body-on-frame construction. This can lead to improved fuel efficiency and performance.
- Better handling: The integrated design of a unibody vehicle can provide better handling characteristics compared to a body-on-frame vehicle. The rigidity of the structure allows for more precise control and responsiveness.
- Enhanced safety: Unibody vehicles often offer improved safety features compared to body-on-frame vehicles. The integrated structure can better absorb and distribute crash forces, reducing the risk of injury to occupants.
- Space utilization: Unibody construction allows for more efficient use of interior space. Without a separate frame, there is more room for passengers and cargo within the vehicle.
- Noisy reduction: The integrated structure of a unibody vehicle can help reduce noise and vibration compared to a body-on-frame vehicle. This can result in a quieter and more comfortable driving experience.
Overall, unibody construction offers numerous advantages in terms of weight, handling, safety, space utilization, and noise reduction. These benefits have made it a popular choice for many modern vehicles.
What is meant by body damage?
Body damage refers to any physical harm or injury sustained by the exterior of a car. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including collisions, accidents, vandalism, or natural elements such as hail or falling debris.
Body damage can range from minor scratches and dents to more severe issues like cracked or shattered windows, bent frames, or significant structural damage. It can affect various parts of the car’s body, including the panels, doors, bumpers, fenders, hood, roof, and trunk.
When a car’s body is damaged, it not only affects the aesthetics but also the functionality and safety of the vehicle. Depending on the extent of the damage, it may impair the car’s performance, compromise its structural integrity, or hinder the operation of essential components such as doors, windows, or the trunk.
Repairing body damage often involves techniques such as dent removal, panel replacement, paintwork, or window replacement. The cost and complexity of the repairs depend on the severity and extent of the damage.
Addressing body damage promptly is crucial to prevent further deterioration and maintain the value and appearance of the car. It is recommended to seek professional help from auto body repair shops or technicians with expertise in repairing and restoring damaged car bodies.
Dents and chips
Dents and chips are common types of damage that can occur to a car’s body. Dents are depressions or indentations in the surface of the body, often caused by impacts from other objects or accidents. They can range in size from small dings to large craters.
Chips, on the other hand, are small areas where the paint or surface layer of the body has been chipped away or damaged. They can be caused by rocks, gravel, or other debris hitting the car while driving. Chips can lead to rust and further damage if not repaired promptly.
Both dents and chips can affect the appearance and value of a car. They can also expose the underlying metal or body material to the elements, which can lead to corrosion and structural issues over time.
Repairing dents and chips often involves techniques such as paintless dent repair, where the dent is pushed out from the inside without the need for repainting. For chips, touch-up paint or professional repainting may be necessary to restore the car’s appearance and protect it from further damage.
Regular maintenance and care can help prevent dents and chips, such as parking in a garage or protected area, avoiding driving too closely behind other vehicles, and using protective films or covers for areas prone to chips.
In conclusion, dents and chips are common types of damage that can occur to a car’s body. They can affect the appearance, value, and structural integrity of the vehicle, but can often be repaired or prevented with the right techniques and care.
Cracks and tears
Cracks and tears are common issues that can occur in a car’s body. They can be caused by various factors such as accidents, age, and wear and tear. Cracks are small openings or fractures in the body, while tears refer to larger openings or splits.
Cracks and tears can be found in different parts of the car’s body, including the exterior panels, fenders, doors, and bumpers. They can also occur in the windshield and windows. These damages not only affect the aesthetic appearance of the car but also compromise its structural integrity and safety.
When cracks and tears are detected, they should be repaired as soon as possible to prevent further damage and ensure the car’s safety. The repair process typically involves filling the cracks or tears with a suitable filler material and then sanding and painting the affected area to match the car’s original finish.
| Causes of cracks and tears | Signs of cracks and tears | Repairing cracks and tears |
|---|---|---|
| Accidents | Visible openings or fractures in the body | Filling with filler material, sanding, and painting |
| Age and wear and tear | Damage to exterior panels, fenders, doors, bumpers, windshield, and windows | Preventing further damage and ensuring safety |
Regular inspection and maintenance of the car’s body can help identify cracks and tears early on and prevent them from worsening. It is also important to address any underlying issues, such as rust or structural damage, to avoid future cracks and tears.
Corrosion
Corrosion is the process of gradual deterioration and damage to a car body caused by chemical reactions with the environment. It is a common problem in vehicles, especially in areas with high humidity or exposure to saltwater or road salt. Corrosion can weaken the structural integrity of the car body and affect its appearance.
The most common type of corrosion in cars is called rust. Rust occurs when iron or steel reacts with oxygen and moisture, forming iron oxide. It usually starts on the surface of the metal and spreads deeper over time. Rust can appear as reddish-brown patches or bubbles on the car body.
There are several factors that contribute to the corrosion process. These include exposure to moisture, salt, chemicals, and pollutants in the air. Scratches, dents, and chipped paint can also accelerate corrosion as they expose the metal underneath to the elements. Poor maintenance and lack of protective coatings can also make a car more susceptible to corrosion.
To prevent corrosion, it is important to regularly clean and wax the car body to remove dirt, salt, and other contaminants. Applying a protective coating, such as a rust inhibitor or an anti-corrosion sealant, can also help to prevent or slow down the corrosion process. It is also recommended to avoid driving on salted roads whenever possible and to promptly repair any scratches or damage to the car body.
If corrosion has already occurred, it is important to take action to stop its progression. This may involve removing the rusted areas, treating them with rust converters or inhibitors, and repainting the affected parts. In severe cases, it may be necessary to replace the corroded panels or structural components of the car body.
Overall, understanding corrosion and taking preventive measures can help prolong the lifespan and maintain the appearance of a car body.
Q&A:
What is the purpose of a car body?
The purpose of a car body is to provide a structure that protects the occupants of the vehicle and supports the various components of the car, such as the engine, suspension, and wheels.
What are the different types of car bodies?
There are several different types of car bodies, including sedans, SUVs, coupes, convertibles, and hatchbacks. Each type has its own unique design and features.
What are some common materials used in car body construction?
Some common materials used in car body construction include steel, aluminum, and carbon fiber. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of strength, weight, and cost.
What is car body aerodynamics?
Car body aerodynamics refers to the study of how air flows around a vehicle. It is an important factor that affects fuel efficiency, stability, and handling. Car designers use various techniques to reduce drag and improve aerodynamic performance.
What is car body styling?
Car body styling refers to the design and aesthetics of a vehicle’s exterior. It includes elements such as the shape of the car, the placement of windows and doors, and the design of the grille and headlights. Car manufacturers often use styling to differentiate their vehicles and create a unique brand identity.
What is a car body?
A car body refers to the main structure of a vehicle, excluding the engine, wheels, and other mechanical components. It is the outer shell of the car that protects the passengers and provides a streamlined shape for aerodynamics.
What are the basic terms related to car bodies?
Some basic terms related to car bodies include chassis, frame, body panels, fenders, hood, trunk, doors, windows, and roof. These terms describe different parts of the car body and their functions.
What is the purpose of car body panels?
Car body panels are designed to provide structural support and protect the interior of the vehicle from external elements. They also contribute to the overall aesthetics of the car and can be made from different materials such as steel, aluminum, or carbon fiber.
What are some common car body styles?
Some common car body styles include sedan, hatchback, SUV, coupe, convertible, and minivan. Each body style has its own unique design and features, catering to different consumer preferences and needs.





